There are countless descendants of dragons who have dreams. They are or will be in Cambodia. They do not pay attention to the relevant laws and regulations of finance and tax. You will be overthrown by sudden attacks, because the speed at which you make money can hardly catch up with a huge legal sanction. (This article is transferred from the Cambodia Investment Guide). This service account insists on originality. The author Zhang Xiaoming, Chairman of Zhuo Zhi Cambodia, three years of multinational enterprise management experience, six years of listing audit experience, five years of entrepreneurial experience, Chinese Certified Public Accountant (CPA), International Certified Public Accountant (ACCA). WeChat: 13928404895, 085502018
The main purpose of this article is to give an overview of the current tax system in Cambodia, introduce the main tax types, and help investors understand the local tax situation, better carry out business activities, avoid tax risks, and make reasonable tax planning. In view of space issues, this article will first introduce 6 tax categories that are extremely closely related to business operations.
This article is mainly for general investment companies, non-qualified investment project (QIP) companies, and qualified investment projects (QIP) to enjoy special tax incentives. If you want to learn about the preferential tax policies applicable to qualified investment projects (QIP), please refer to another article in this official account "Can Chinese investment in Cambodia be tax-free for nine years? 》
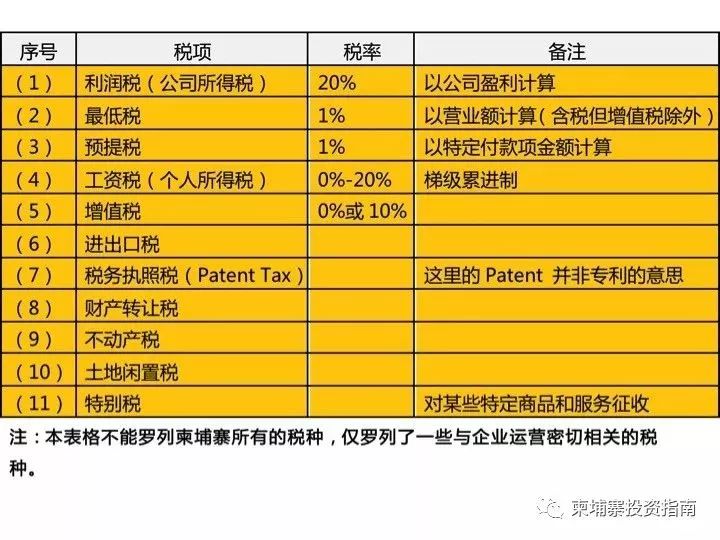
一、 The main taxes involved in investing in Cambodia
二、Cambodian tax system
1. Taxation system
Cambodia’s tax system is a self-declared tax system, which was officially used in 2016. Under this system, taxpayers are divided into three types: small taxpayers, medium taxpayers and large taxpayers. Small taxpayers are mainly suitable for local small family businesses. As a foreign investor, you can only file a tax declaration as a medium-sized taxpayer or a large taxpayer.
2. Collection management agency
The General Administration of Taxation of Cambodia exercises the responsibility of tax collection and management. The State Administration of Taxation consists of the Taxation Section, the Dispute Resolution Section, the Investigation Section, the Tax Collection Section, the Arrears Collection Section, the Audit Section and the Audit Section. Among them, the investigation section is responsible for investigating whether the company has applied for tax certificates, whether tax evasion or tax evasion; the audit section is responsible for auditing financial statements and has the right to remove unreasonable expenditures and enter the accounts
三、Introduction of main taxes
1. Profit tax
Profit tax (for corporate legal persons), any legal person that organizes and operates various commercial activities and cooperative operations in Cambodia or whose main place of business is in Cambodia is subject to profit tax. The standard tax rate is 20%, and the tax rate on development profits of oil and natural gas and natural resources is 30%.
Profit tax is paid in advance on a monthly basis, which is mainly 1% of monthly operating income (including all taxes and fees except value-added tax), which is paid before the 20th of each month. The monthly prepayment part can offset the annual profit tax. If the total profit tax paid in each month is approximately the annual profit tax, the excess part can be offset against the profit tax for the next year.
Profit tax is declared in the form of annual tax and must be submitted within 3 months after the end of each fiscal year. The profit tax paid by the company each month can offset the profit tax.
During the tax year, expenses are deductible, but they must be supported by valid bills and documents.
The current "Agreement between the Government of the People's Republic of China and the Royal Government of Cambodia on the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Prevention of Tax Evasion on Income" will be officially applied on January 1, 2019. Corporate profits from China or Cambodia can be subject to regulations to avoid double taxation.
2. Minimum tax
The minimum tax is an annual tax, equivalent to 1% of the annual operating income (including all taxes except value-added tax). If the minimum tax amount is greater than the taxpayer's profit tax amount, it will apply. It does not consider whether the taxpayer makes a profit or loses money. The minimum tax declaration deadline is the same as the profit tax declaration deadline. All are within 3 months after the end of the tax year.
The relationship between minimum tax and profit tax
If the profit tax amount exceeds the minimum tax amount, the taxpayer pays only the profit tax. If the profit tax amount is less than the minimum tax amount, the taxpayer only pays the minimum tax. The taxpayer's monthly profit tax can offset the minimum tax.
Starting from January 1, 2017, the new decree stipulates that only those taxpayers who have not been able to maintain financial vouchers are required to pay the minimum tax. The decree defines the concept of whether financial vouchers are well maintained. There is a certain degree of uncertainty in the current operation. In practice, the tax bureau requires the company to provide audited financial statements.
The prepaid profit tax and withholding tax paid by taxpayers can offset the minimum tax.
3. Withholding tax
Withholding tax needs to be withheld in specific payments.
Types of withholding tax:
1. Rent: 10%
2. Service: 15%
3. Remuneration: 15%
4. Interest: 15% (not applicable to repayment to local Cambodian banks)
5. Fixed deposit interest: 6% (only applicable to Cambodian bank deposits)
6. Current deposit interest: 4% (only applicable to Cambodian bank deposits)
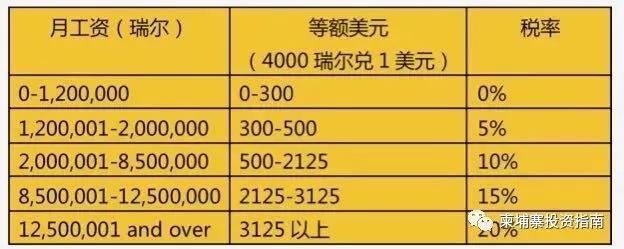
4. Payroll tax
Cambodia levies payroll tax based on residence and source of income as the main principles. As a Cambodian resident, his global income should be collected in accordance with Cambodian tax laws. For non-residents, only income from Cambodia is subject to payroll tax. The place where wages are paid is not related to the source of wages. The current "Agreement between the Government of the People's Republic of China and the Royal Government of Cambodia on the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Prevention of Tax Evasion on Income" will be officially applied on January 1, 2019. Personal income from China or Cambodia can avoid double taxation according to regulations.
5. Value Added Tax
In Cambodia, the sales of goods and the provision of services are subject to value-added tax. All corporate legal persons must complete VAT registration before starting business. The value-added tax adopts a uniform rate of 10%.
VAT exemption:
1. Public Postal Service
2. Hospital medical services
3. Public transportation services operated by the state
4. Major financial services (not defined)
5. Import of specific personal items
6. Non-profit activities for the public interest
7. Educational Services
8. Supply of electricity and clean water
9. Unprocessed agricultural products
10. Collection and removal of solid and liquid waste
6. Import tax: The import tax rate is 0%-35%.
As one of the ASEAN member states, Cambodia should reduce import taxes to between 0% and 5% in accordance with the agreement between the member states.
7. Export tax: Only levied on certain export goods, such as timber, animal products (including most seafood)





