This service account insists on originality. The author is Zhang Xiaoming, partner of Zhuozhi (Cambodia) Accounting Firm, three years of multinational enterprise management experience, six years of listing audit experience, five years of entrepreneurial experience, Chinese certified public accountant (CPA), international certified public accountant (ACCA) ). WeChat: 13928404895, 085502018
Cambodia's foreign trade laws and regulations and its investment environment
The legal framework of Cambodia's foreign trade
● Trade authority
The Ministry of Commerce of Cambodia is the competent authority for trade in Cambodia.
● Trade law system
Cambodia’s trade-related laws and regulations mainly include the "Import and Export Commodity Tariff Management Law", the "Regulations on the Issuance of Certificates of Origin, Commercial Invoices, and Export Licenses in the Clothing Industry", "Regulations on the Trade Behavior of Commercial Companies", and "Regulations on the Issuance of Certificates of Origin, Commercial Invoices and Export Licenses in the Clothing Industry" Implementation of the Provisions on Pre-shipment Inspection Services, the WTO Accession Act, the Sub-decree on Risk Management, and the Provisions on the Establishment of the Risk Management Office of the Customs and Taxation Administration, etc.
● Relevant regulations on trade management
The Ministry of Commerce is responsible for export approval and tax-free import approval procedures. In most cases, no license is required to import goods. However, some products can only be exported after obtaining special export authorization or permission from relevant government departments.
| Export preferences as a least developed country
As a least developed country, 28 countries or regions including Europe, the United States, and Japan have granted Cambodia GSP treatment. The United States has granted Cambodia relatively loose quotas and import tariffs. Under the "All Commodities Except Arms Initiative", the European Union has granted zero tariffs to Cambodia on almost all products except arms.
| The local content and origin principle of export commodities
Cambodia currently has no local content requirements, that is, it does not restrict the use of imported raw materials and parts (except raw materials and parts that are harmful to health, the environment or the society). In Cambodia, exporters should pay attention to the rules of origin requirements of the GSP. For products exported to the United States under the Generalized System of Preferences, the minimum requirement for local content in the rules of origin is 35% (eligible ASEAN member states, namely Cambodia, Thailand, Indonesia and the Philippines, are regarded as the same country in the requirements of the rules of origin). Under the "All Commodities Except Arms Initiative", the rules of origin require that at least 40% of the content of exported products originate from the exporting country.
| Export Preferential
According to the Investment Law Amendment Act, export-oriented qualified investment projects approved by the Cambodia Investment Commission can enjoy tax holidays or special depreciation. The value-added tax of its export products enjoys tax rebate or is credited to the raw materials of export products.
| Export restrictions
Prohibited or strictly restricted export products include cultural relics, narcotics and toxic substances, logs, precious metals and gems, weapons, etc. In early 2013, the Cambodian government explicitly banned the trade and circulation of rosewood. Semi-finished or finished wood products, rubber, raw or cooked skins, fish (fresh, frozen or sliced) and live animals are subject to a 10% export tax. Apparel exports need to pay management fees to the Ministry of Commerce. Clothing exported to the United States or the European Union under the Generalized System of Preferences must obtain an export permitProvable.
| Duty Free Import
According to the Investment Law Amendment Law, export-oriented qualified investment projects approved by the Cambodian Investment Commission can import production equipment, construction materials, raw materials and production input accessories tax-free. In order to obtain the duty-free import approval documents for raw materials for production, the importing company should declare the quantity and value of the materials to be imported to the Cambodia Investment Commission every year.
● Import and export commodity inspection and quarantine
The Customs and Customs Administration of the Ministry of Finance and the Import and Export Inspection and Anti-fraud Bureau of the Ministry of Commerce are jointly responsible for the inspection of imported and exported commodities. The inspection location is the factory or import and export port. At present, all import and export goods in Cambodia are subject to inspection, and the government is planning to reduce the inspection rate year by year. Imported goods valued at US$5,000 or more are subject to pre-shipment inspection in the exporting country. The inspection report and other pre-shipment inspection documents will be submitted to the Cambodian Customs. After the goods arrive in Cambodia, the consignor will present the inspection documents to the Customs to pay the tax and submit the goods.
● Customs management rules and regulations
The Cambodian government has continuously improved its customs management system in recent years, and is committed to achieving concise, efficient, transparent and predictable customs management. In 2006, Cambodia drafted and passed the "Sub-decree on the Implementation of Trade Facilitation through Risk Management", preparing to implement a risk management system based on trader file data, that is, by using computer systems to analyze trader file data, commodities and/or The place of origin is subject to customs supervision. To this end, the Cambodian government has also adopted a computerized integrated customs clearance system-automatic customs data system. Under the common effective tariff system of the ASEAN Free Trade Agreement, products imported from other ASEAN member countries that meet the rules of origin can enjoy lower tariff rates. According to the overall tariff reduction schedule, by 2010, except for a few special commodities, Cambodia's tariff rate will be reduced to 0-5%.

Market access for foreign investment
● Investment authority
The Cambodian Development Council is the only one-stop service organization responsible for reconstruction, development and investment supervision affairs. It is composed of the Cambodian Reconstruction and Development Commission and the Cambodian Investment Commission. This agency is responsible for evaluating and making decisions on all reconstruction, development work and investment project activities, approving qualified investment projects for which investors have applied for registration, and issuing final registration certificates. However, investment projects with the following conditions must be submitted to the Cabinet Office for approval: (1) The investment amount exceeds US$50 million; (2) Politically sensitive issues are involved; (3) The exploration and development of minerals and natural resources; The environment has adverse effects; (5) Infrastructure projects, including BOT, BOOT, BOO and BLT projects; (6) Long-term development strategy.
● Regulations of the investment industry
The Cambodian government regards foreign direct investment as the main driving force for economic development. Cambodia does not have a special foreign investment law, and basically gives equal treatment to foreign investment and domestic investment. Its policy is mainly reflected in the "Investment Law" (this law was passed at the first special session of the Kingdom of Cambodia on August 4, 1994, 1997 and 1999). Revised twice a year) and its "Amendment Law" (passed by the Second Parliament of the Kingdom of Cambodia on February 3, 2003) and other relevant laws and regulations.
| Areas to encourage investment
Article 12 of the "Investment Law" stipulates that the Cambodian government encourages investment in key areas including: innovation and high-tech industries; job creation; export-oriented; tourism; agro-industry and processing; infrastructure and energy; provincial and rural development ; Environmental protection; Investment in special development zones established in accordance with the law. Investment incentives include exemption from all or part of customs duties and taxes.
| Restricted areas of investment
The “Implementation Rules of the Investment Law Amendment Law” (promulgated on September 27, 2005) lists the investment activities that Cambodia and foreign entities are prohibited from engaging in, including: nerve and narcotic substance production and processing; the use of international rules or the World Health Organization prohibits the use of, Chemical substances that affect public health and the environment produce toxic chemicals, pesticides, pesticides and other products; use foreign imported waste to process power generation; forest development business prohibited by the forest law; other investment activities prohibited by the law.
In addition, the rules also listed "investment activities that do not enjoy investment preferences" and "specific investment activities that can be exempt from tariffs but do not enjoy corporate profits tax exemption."
| Restrictions on foreign citizens
The "Investment Law" stipulates the ownership and use of land: (1) The ownership of land used for investment activities must be owned by a Cambodian natural person, or a Cambodian natural person or legal person that directly holds more than 51% of the shares; (2) ) Investors are allowed to use land through concessions, indefinite long-term leases, and renewable short-term leases. Investors have the right to own immovable and private property on the ground and use them as collateral.
● Regulations on investment methods
| Foreign Direct Investment
Investment activities in Cambodia are relatively loose and are not restricted by nationality (except for the provisions of the Land Law on land property rights). Except in areas where foreigners are prohibited or restricted from entering, foreign investors can register with the Ministry of Commerce in the form of individuals, partnerships, companies and other commercial organizations and obtain relevant business licenses to freely implement investment projects. However, projects that intend to enjoy investment incentives can only be implemented after applying for investment registration with the Cambodia Development Council and obtaining the final registration certificate. Investment projects that have been approved for investment are called "qualified investment projects".
| Joint Venture
Qualified investment projects can be established in the form of joint ventures. A joint venture can be composed of Cambodian entities, Cambodian and foreign entities or foreign entities. Royal government agencies can also act as joint venture parties. There are no restrictions on the nationality or shareholding ratio of shareholders, except for joint ventures that own or intend to own land or land rights in the Kingdom of Cambodia. In this case, the total maximum shareholding ratio of natural or legal persons of non-Cambodian entities shall not exceed 49%.
| Consolidation of Qualified Investment Projects
Two or more investors, or the investor and other natural or legal persons agree to merge to form a new entity, and the new entity intends to implement the investor’s qualified investment project and enjoy the investment incentives and investment protection specified in the final registration certificate of the qualified investment project, the new entity It is necessary to apply to the Investment Committee for registration as an investor in writing and to transfer the final registration certificate of qualified investment projects to a new entity.
| Acquisition of qualified investment projects
If an investor or other natural or legal person acquires the ownership of a qualified investment project and intends to enjoy the investment incentives and investment protection stipulated in the final registration certificate of the qualified investment project, it shall submit an application for acquisition to the Investment Committee and transfer the final registration certificate of the qualified investment project to a new entity. If the acquirer is an unregistered natural person or legal person, it must first apply for registration as an investor. If the transfer of the investor’s shares causes the transferee to obtain the investor’s control, the investor must file an application for the transfer to the Investment Committee and provide the transferee’s name and address.
● BOT method
Currently, BOT projects in Cambodia are mainly based on Chinese-funded companies, and the industries involved include hydropower stations, transmission and transformation grids, etc. There are no special regulations on the concession period, and the operating period of hydropower stations is generally 30-40 years. The Ganzai Hydropower Station project invested by Sinohydro Group is Cambodia's first BOT project. It started construction in April 2006 with a total investment of 260 million US dollars. The concession operation period is 44 years, of which the construction period is 4 years and the operation period is 40 years.
●Investment preferential policies
The Cambodian government gives foreign investment and domestic investment basically the same treatment. The Investment Law (adopted at the first special session of the Kingdom of Cambodia on August 4, 1994) and its amendment laws (two amendments in 1997 and 1999) provide foreign investment In order to guarantee and relatively preferential taxation and land lease policies. In addition, foreign investment can also enjoy the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) granted to Cambodia by 28 countries or regions including the United States, Europe, and Japan.
● Investment protection
The investment protection provided by the Cambodian government to investors includes: (1) Basically giving equal treatment to foreign and domestic capital. All investors, regardless of nationality and race, are equal before the law; (2) The Cambodian government does not impose damages on investors The nationalization policy of property; (3) The Cambodian government does not control product prices and service prices for approved investment projects; (4) No foreign exchange control is implemented, allowing investors to purchase foreign exchange from the banking system and transfer them abroad for use Liquidate its financial debts related to investment activities.
● Investment incentives
The investment incentives that can be obtained for qualified investment projects approved by the Cambodia Development Council include: (1) Exemption of import tariffs on production equipment, construction materials, spare parts and raw materials of the investment production enterprise; (2) The enterprise can enjoy 3 -8 years of tax holiday (for special economic zones up to 9 years), after the tax holiday, a corporate profit tax rate of 9% is paid according to the tax law; (3) Profits are used for reinvestment, and corporate profit tax is exempt; dividends are not distributed Taxation; (4) Export products are exempt from export tax.

Related procedures for Chinese residents (enterprises) to invest in Cambodia
● Procedures for investing and registering a company in Cambodia
Any enterprise engaging in commercial activities in Cambodia must be registered, otherwise it will be punished as the crime of illegally engaging in commercial activities.
● Forms of setting up a business
The environment for conducting economic and trade activities in Cambodia is relatively relaxed, and the business standards are relatively low. It can be registered in various forms of business organizations such as individuals, partnerships, and companies.
● Acceptance agency of registered enterprises
The Ministry of Commerce of Cambodia is responsible for the management of the "Industrial and Commercial Register", and enterprises should register with the Commercial Registration Office of the Ministry of Commerce of Cambodia or the Industrial and Commercial Registry designated by the Ministry of Commerce before establishment. Companies that set up a branch or representative office in Cambodia should also register with the Commercial Registration Office of the Ministry of Commerce.
If enterprises or individuals engaged in investment in Cambodia need to obtain investment incentives, they should first submit an investment application to the Cambodia Development Commission (CDC) and obtain a conditional registration certificate before registering.
● The main procedures for registering a company
| Registration application
A director or shareholder of an enterprise should personally go to the competent authority to fill in the registration form and submit an application. The Commercial Registry of Cambodia can provide the registrant with the blueprint of the company's articles of incorporation. The documents to be submitted for registration include: registration application form, articles of incorporation, document verification, application for advertisement in designated publications, copies and photos of ID cards or passports of all directors or shareholders, certificates of non-criminal record of directors, and equity distribution Decisions (if natural persons are involved), office location, and other documents required by the Ministry of Commerce.
| Registration Approval
After the competent authority accepts the registration application, it will issue a registration certificate marked with a registration number. The certificate is a temporary certificate within one month from the date of issuance. During this period, if the registrar finds that the application materials are incorrect, he can raise an objection and revoke the registration number. The registration approval time depends on the specific situation, generally one week. The registration fee depends on the form and size of the company.
| Registration time limit
The registration certificate is valid for 3 years from the date of registration. Enterprises should reapply for a new certificate within 30 days before the expiration of the registration certificate. If an enterprise delays in applying for a new certificate, it will be deemed illegal, and its original certificate will become invalid, and the enterprise must re-apply for registration and pay the relevant fees.
| Open a bank account
Registered companies should open one or more bank accounts in Cambodian banks.
● Procedures for contracting engineering projects
| Get information
National projects are released by various competent departments; all provinces and major cities also release project information in their respective regions. In addition, major newspapers and periodicals also regularly publish bidding information.
| Bidding
All Cambodian national investment projects or international organization loans and assistance projects will be tendered. The basic procedures for bidding include:
(1) Preparation stage: design and cost estimate; submit the design and cost estimate to the bank, solicit the bank’s opinion and get approval; prepare the bidding documents; submit the bidding document to the bank, solicit opinions and get approval.
(2) Qualification pre-selection stage: invitation to participate in the pre-qualification (advertisement in the newspaper); the evaluation committee evaluates the pre-qualification; the pre-qualification evaluation is reported to the Ministry of Finance and Economics for approval; the pre-qualification evaluation is reported to the bank for approval; the contractor is notified of the result of the pre-qualification; Identify contractors who meet the pre-qualification criteria.
(3) Bidding and evaluation stage: bidding; contractor prepares bidding; bid opening; bid evaluation committee evaluates bids; bid evaluation results and bid award recommendations are reported to the Ministry of Finance and Economics for approval; bid evaluation results and bid award recommendations are reported to the bank for approval; contract is signed .
(4) The stage of selecting the final selection list: the invitation to explain the fee rate; the consultant or the supervisor prepares the explanation of the fee rate; submits the fee collection instructions to the project execution department; the evaluation committee evaluates the fee collection instructions; the company's final selection list is submitted to the Ministry of Finance and Economics for approval ; The company's final election list is submitted to the bank for approval.
(5) Plan preparation stage: Invite companies in the short list to propose plans: companies in the short list prepare plans; submit plans.
(6) Technical and financial evaluation stage: The evaluation committee evaluates the technical plan; the technical plan is submitted to the Ministry of Finance and Economics for approval; the technical plan is submitted to the bank for approval; The bid award proposal with the highest comprehensive score of the technical plan and the financial plan shall be submitted to the Ministry of Finance and Economics for approval; the bid award recommendation with the highest comprehensive score of the technical plan and the financial plan shall be submitted to the bank for approval; the contract shall be signed.
|License procedures
Contracting projects in Cambodia need to provide the company’s qualification certificate, the foreign contracted project right certificate issued by the home country, the registration certificate of the Cambodian Ministry of Commerce and the performance guarantee provided by the bank, and must go through the bidding review, and must pass the bid evaluation and win the bid.

Matters needing attention for Chinese residents (enterprises) to carry out investment cooperation in Cambodia
● Investment
| Accurately grasp Cambodian investment policies and regulations
Enterprises must first know the law and the law to carry out investment activities. It is necessary to fully grasp the laws and regulations related to investment in Cambodia, and accurately grasp the government's policies on investment protection, investment preferences and restrictions, foreign exchange, land use, and business organization forms.
| Objectively analyze the comparative advantages of investment in Cambodia
The main advantages of investing in Cambodia include: (1) The implementation of an open free market economy policy and a high degree of liberalization of economic activities; (2) The government is the main driving force for foreign direct investment, and investment-related laws and regulations are based on encouraging foreign investment. , Foreign investment basically enjoys the same treatment as domestic investment; (3) Cambodia is rich in natural resources, rich in minerals, water conservancy, agricultural products, fishery, etc., which will provide enterprises with more investment opportunities. The main unfavorable factors for investing in Cambodia include: poor infrastructure conditions such as water, electricity, transportation, and communications, and high related costs; compared with neighboring textile and garment competitors such as Vietnam and Bangladesh, workers’ wages are higher.
In addition, the soft investment environment in Cambodia needs to be improved. It is mainly reflected in: (1) Government departments spend a long time working on affairs, and trade unions organize strikes and demonstrations more frequently; (2) The market and business order need to be improved. Cambodia has not established an economic court, and the protection of foreign investment in accordance with the law needs to be improved; (3) Cambodia's economic development mainly depends on foreign aid and foreign investment.
| Avoid investment risks
Companies can take the following measures to avoid investment risks: (1) Comprehensively understand information and improve the quality of decision-making. Proactively contact Chinese business institutions in Cambodia, obtain information through formal channels, conduct in-depth national conditions and market research, fully understand investment risks before making investment decisions, and prevent decision-making errors; (2) Keep a clear mind and implement everything. The unacceptable words of the enterprise shall be subject to the official approval of the government for all promises. When choosing a partner, the background and strength should also be examined first.
● Trade
Doing business in Cambodia is not restricted by nationality, but Chinese companies and personnel must be familiar with and adapt to the special local trade environment and take effective measures to expand their business.
| Familiar with the main features of Cambodian trade
Cambodia's industrial production is dominated by the garment industry with two ends outside, so its import and export trade has the following distinctive characteristics: (1) Industrial finished products and garment processing raw materials are almost entirely imported, and most of the export products are garments; (2) ) Foreign-invested garment processing enterprises are the main force for the growth of foreign trade. In recent years, Cambodia's garment exports accounted for more than 95% of total exports; (3) The main export markets are the United States and Europe, and the main sources of imports are ASEAN and East Asia. In recent years, imports from ASEAN countries have increased rapidly.
| Understand the advantages and constraints of Cambodian trade
Advantages: (1) Cambodia joined the ASEAN in 1999, and the ASEAN member states will follow the steps to achieve the goal of tariff reduction under the common and effective preferential tariff system. In November 2002, China and ASEAN signed the "China-ASEAN Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement." In early 2010, the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area was fully established, and the "early harvest" tax reduction and exemption plan for Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar was granted. Among them, Preferential treatment for imports of 418 kinds of commodities (mainly agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, and plant products) in Cambodia is granted zero tariff. In addition, the construction of new free trade areas between ASEAN and India, South Korea, Japan, and Australia is also underway. The process of ASEAN economic integration and the construction of a free trade area will, to a large extent, promote the development of Cambodia’s economy and foreign trade. (2) 28 countries/regions including the United States, the European Union, and Japan have granted Cambodia’s Generalized System of Preferences (GSP); for the import of textile and apparel products from Cambodia, the United States grants looser quotas and reduces or exempts import tariffs. The European Union does not impose restrictions, Canada offers preferential measures such as exemption of import tariffs. Constraints include:(1) Cambodia's trade structure is single, mainly exporting ready-made garments and concentrated in the US and European markets. It is vulnerable to changes in the international economic environment, especially the economic situation in the US and Europe. On the one hand, the global financial crisis has led to economic recession in Europe and the United States and reduced imports, affecting Cambodia’s garment exports; on the other hand, the rise in world grain and oil prices has led to a substantial increase in the cost of garment enterprises and a decrease in profitability. (2) Cambodian garment exports can still enjoy preferential treatment, but will face the challenges of increasingly equal treatment and free competition in the future. Compared with Cambodia, Vietnam and other neighboring countries have obvious competitive advantages in terms of labor costs and expertise. After sub-Saharan African countries' textile and apparel exports have received quota-free and tariff-free treatment from the United States, their exports have grown rapidly. (3) Cambodia's garment industry has approached saturation, and this industry has become increasingly difficult to attract new investment, which has led to a decrease in the amount of foreign investment in the garment industry in recent years.
| Flexible use of tax rules
Cambodia currently has the following tax types and tax rates: profit tax 9% or 20%, value-added tax 10%, and business tax 2%. The main taxes and tax rates levied on private investment enterprises in Cambodia are: 9% profit tax, 10% value added tax, and 2% business tax.
| Focus on improving product quality
Quality is credibility and the foundation of a company's survival. The products exported by Chinese companies to Cambodia mainly include textiles and their raw materials, machinery, electrical appliances, food, auto parts, construction materials, medicine, tobacco and chemical products. Chinese companies should focus on improving the quality of export products and build a good international reputation.
● In terms of contracting projects
| Seize market opportunities
Vigorously developing infrastructure construction has become one of the important economic goals of the Cambodian government. The World Bank and the Asian Development Bank provide Cambodia with nearly 100 million U.S. dollars in concessional loans each year, mainly involving technical support, electricity, water supply and drainage, roads and airports and other infrastructure construction, health, agriculture, poverty reduction and education. Chinese companies should seize the opportunity of Cambodia's infrastructure construction and vigorously explore the Cambodian engineering market.
| Choose a contracting method
Considering that the Cambodian government urgently needs a large amount of funds to construct infrastructure projects to meet the needs of international competition, Chinese companies should choose some projects with good prospects, and use BOT, BOO and other methods to carry out capital contracting, and use this to drive China's electromechanical equipment and complete sets Export of equipment and labor.
| Select the contract project
Chinese engineering contracting enterprises should step up the training of talents, especially the training of high-quality and high-tech talents. To give full play to their own advantages, choose projects with strong professionalism and high technical requirements, and try to participate in the competition of engineering consulting projects.
| Further market development
While undertaking the Chinese government’s aid to Cambodia’s complete set of projects, Chinese enterprises should establish a good corporate image, lay a foundation for taking root in the local market, increase their competitive advantages in international bidding, and further expand the Cambodian contracted engineering market.
| Carry out healthy competition and cooperation
Chinese enterprises must adhere to the following principles when participating in competition and compiling quotations: technically within their capabilities, economically profitable, and controllable risks in the implementation of the project. Avoid blind and vicious competition. Enterprises should also carry out flexible and diverse cooperation, jointly develop the Cambodian market, and try to avoid fighting alone or fighting each other.
● In terms of labor service cooperation
| Understand the status quo of China-Cambodia labor cooperation
Cambodia is one of the important markets for China to dispatch labor services. In addition to some Chinese laborers brought out by investment and contracting projects in Cambodia, with the development of the Cambodian garment industry, China has exported a large number of skilled labor such as garment processing to Cambodia, mainly distributed in dozens of companies in China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. In garment factories, most of the laborers are garment mechanics, instructors and skilled operators. In addition, some laborers are distributed in construction and service industries. The order of the Cambodian labor market has yet to be rectified, and some illegal businessmen use improper means or unrealistic labor projects to defraud Chinese laborers to go to Cambodia. As a result, the problem of illegal employment in Cambodia is more serious and various labor disputes occur frequently. Relevant Chinese authorities have repeatedly taken measures to strengthen management and publicly issued announcements in the media, requiring relevant enterprises and labor personnel to go through formalities for migrant workers in Cambodia through proper and legal channels, but this problem is still relatively serious.
| Familiar with labor policy
The main basis for the Cambodian government to manage foreign workers is the "Labor Law" promulgated in 1997 and the "Announcement on the Application Method for Employment of Foreigners to Cambodia" issued by the Cambodian Ministry of Labor in January 2002. The relevant Cambodian labor policy department is constantly developing and changing, but its principle is always: strictly control the import of foreign labor, actively implement the strategy of localization of technical talents, do everything possible to solve the problem of a large surplus of domestic labor, and strive to find foreign employment markets.
| Companies must employ labor in accordance with the law
If you hire Chinese workers, you must comply with the relevant regulations of the Ministry of Commerce of China, go through the formalities for migrant workers in Cambodia through proper and legal channels, and prohibit illegal employment. Companies must also apply to the Cambodian Ministry of Labor before the end of November every year for the next year's quota for hiring foreign workers. If they do not apply for the annual quota, they will not be allowed to hire foreign workers. The foreign workers hired must also meet all the conditions stipulated in the Labor Law.
| Actively explore new areas
Facing China’s largest labor cooperation field in Cambodia-the textile and garment industry has been shrinking, while continuing to consolidate the traditional labor market, China’s key areas of labor export should be changed, and China should actively develop tourism, agriculture, and Chinese. Education and vocational training projects and other labor cooperation fields.
| Go through relevant procedures in accordance with the law
In the process of applying for a work permit, you should first carefully understand the laws and regulations. Generally speaking, Cambodia’s labor regulations are formulated in full reference to the labor standards of western developed countries, and the requirements are relatively strict, and many regulations are quite different from China’s domestic regulations. When Chinese companies invest in Cambodia and involve labor issues, they must carefully read the relevant laws and regulations to avoid labor issues.
There are many requirements for applying for work permits and employment cards in Cambodia, and the procedures are more complicated. It is recommended that Chinese enterprises and related personnel hire local lawyers or intermediaries with extensive experience to assist in the relevant procedures.
● Other matters needing attention
From May to November each year is the rainy season in Cambodia. Heavy rain falls across the country. In some areas, local residents and foreign tourists have been washed away by floods. Therefore, the Chinese Embassy in Cambodia reminds Chinese citizens in Cambodia to pay attention to the latest developments and personal safety at all times. In case of emergency, you can contact the embassy. The 24-hour consular insurance duty phone number of the consular department of the embassy in Cambodia: 00855-12901937, 00855-12901923.
● Prevent investment cooperation risks
In the process of investment, trade, contracted projects and labor cooperation in Cambodia, special attention should be paid to prior investigation, analysis, and evaluation of related risks, and risk avoidance and management should be done in the event to effectively protect one's own interests.Including the credit investigation and evaluation of the project or trade customers and related parties, the analysis and avoidance of the political and commercial risks of the country where the project is invested or contracted, and the feasibility analysis of the implementation of the project itself. It is recommended that relevant companies actively use the relevant businesses of insurance financial institutions such as insurance, guarantees, banks and other professional risk management institutions to protect their own interests. At present, some policy insurance institutions and policy banks can provide credit risk protection products and commercial guarantee services, including trade, investment, contracted engineering and labor credit insurance, property insurance, personal safety insurance, etc., as well as the bank’s factoring business and welfare insurance. Feting business, all kinds of guarantee business (government guarantee, commercial guarantee, letter of guarantee), etc. If a risk loss occurs without effective risk aversion, the loss should be recovered as soon as possible through its own or related means according to the loss situation. For the business underwritten by credit insurance institutions, the credit insurance institution will determine the loss and compensate for the risk loss, and the relevant institution will assist the credit insurance institution in recovering the compensation.

Cambodia's basic tax system
Cambodia's basic taxation legal system
Cambodia implements a unified national tax system and adopts a territorial tax system. The Tax Law promulgated in 1997 and the Tax Law Amendment Law promulgated in 2003 provide a legal basis for Cambodia's tax system. In 2004, the Ministry of Finance and Economics also issued the Ministerial Decree on Corporate Profit Tax. This Ministerial Decree is very important for understanding most Cambodian tax regulations because it defines many terms in other tax regulations. The Tax Law is more applicable to most regulations. At the same time, the "Commercial Law", "Customs Law" and "Investment Law" are also important legal texts, and to a large extent they are related to tax matters. They have formulated rules and incentives for investment and foreign trade in Cambodia.
Major tax incentives
| Investment Encouragement Policy
According to the "Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Amendment Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia Investment Law" promulgated in September 2005, the Cambodian government provides the following tax incentives to enterprises that meet the government's encouragement of investment projects:
(1) After the investment enterprise has made a profit, it is exempted from corporate profit tax for 3 years; after that, depending on the investment industry, the investment enterprise can also have an additional tax exemption period of 2 to 5 years.
(2) Qualified investment enterprises can be exempted from tariffs on imported production equipment, raw materials, construction materials, etc.
| Reinvestment preferential policies
The Cambodian government grants accelerated depreciation tax incentives to enterprises that meet the investment projects encouraged by the government and reinvest their profits in Cambodia.
| Special economic zone tax incentives
Enterprises that invest and develop in the special economic zones set up by the Cambodian government can enjoy the treatment of exemption from corporate profit tax, and the tax exemption period is up to 9 years; the import equipment and construction materials required for infrastructure construction in the zone can be exempted Import tariffs.
Taxation types in the Kingdom of Cambodia
Any company operating in the Kingdom of Cambodia, including a qualified investment company approved by the Cambodia Development Council, may be subject to the following taxes after its incorporation:
(1) Registration tax
(2) Tax license tax
(3) Profit tax
(4) Business tax
(5) Dividend tax
(6) Withholding tax
(7) Minimum tax
(8) Payroll tax
(9) Value-added tax
(10) Specific goods and services tax
(11) Stamp duty
(12) Unused land tax
(13) Public lighting tax
Cambodia's basic taxation legal system
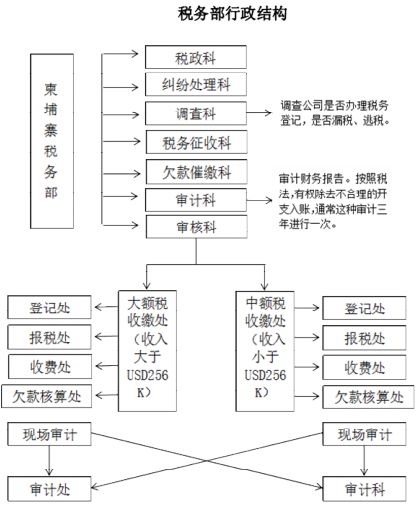
The Ministry of Taxation of Cambodia exercises the responsibility of tax collection and management. Its administrative structure is: Tax Administration Section, Dispute Resolution Section, Investigation Section, Tax Collection Section, Arrears Collection Section, Audit Section and Audit Section. Among them, the investigation section is responsible for investigating whether the company has applied for a tax certificate, whether tax evasion or tax evasion; the audit section is responsible for auditing financial reports, and has the right to remove unreasonable expenses into the account. This type of audit is usually conducted once every three years. The specific administrative structure is shown in Figure.
Filing requirements and tax payment
| Cambodia's tax declaration regulations
(1) The company must register with the taxation department within 15 days after the registration of the Ministry of Finance and Economics.
(2) After the company has received the business tax and value-added tax certificates, it must start tax filing in the month when the value-added tax certificate is issued.
(3) All taxes must be reported within the prescribed time limit.
(4) Due to the need of the annual review, the company must prepare the tax filing materials for the previous tax year before March 31 of the next year.
(5) Corporate profit tax must be paid each year before March 31 of the next year.
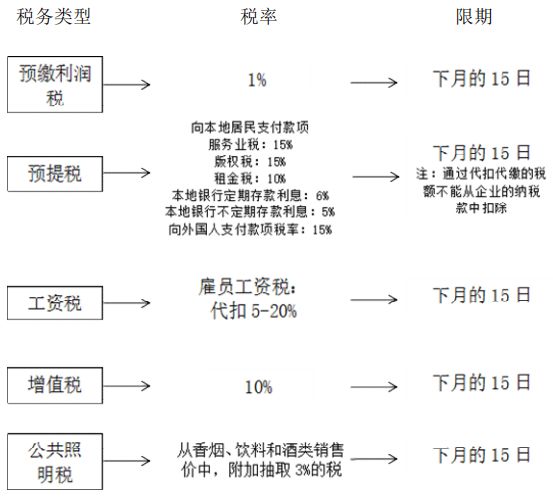
| Taxes to be reported every month
The following are the tax items that the company is obligated to bear: (1) Prepaid corporate profit tax; (2) Personal income tax; (3) Withholding tax; (4) Value-added tax; (5) Public lighting tax (if any); (6) Special tax (if any).
The types of taxes to be reported each month and their tax rates and deadlines are shown in the figure.
● The specific requirements for taxpayers to submit tax information to the taxation department are as follows:
(1) The taxpayer or the withholding agent must submit a tax report to the tax authority, and the report must be submitted in accordance with the form, time and place required by the tax authority.
(2) The report submitted to the taxation department must be signed by the taxpayer or its legally designated agent.
(3) All investors must submit tax reports on a monthly basis and tax reports for the tax year each year.
(4) When submitting the annual tax report, all investors should attach a certificate of compliance with the operational specifications issued by the Cambodia Development Council.
● Taxpayers should keep documents related to finances
Taxpayers shall keep accounting books, related documents and other financial documents in accordance with regulations, and present them to the handling personnel for review when the tax administrative agency requires review. For those accounting books that are not required to be kept in the Cambodian Accounting Law, taxpayers must also keep a running account book, record the income and expenses of each transaction according to the order of year, month and day, and record it in the manner required by the taxation department .
● Taxpayer acceptance notice
To ensure that taxpayers pay various taxes, the taxation department can issue notices to taxpayers or third parties. The notice usually indicates the information that the taxpayer is required to provide, including the taxpayer’s supplier, customer or bank account information. The taxpayer shall personally go to the taxation department to provide the information, documents and data specified in the notice according to the time and place specified in the notice.
● Payment of taxes
The tax payment procedure is as follows:
(1) The tax payable when it is due must be reported to the taxation department within the time specified in the tax clause.
(2) Taxes due and payable must be paid within 30 days after the notification of tax payment is issued.
(3) If there are sufficient reasons to prove that the taxpayer has difficulties in paying taxes, the tax administration agency may conduct tax assessments on the taxpayer. Taxpayers who are due should pay the tax within three days after the notice is sent.

Tax dispute resolution procedures
Currently, Cambodia does not have a tax dispute resolution mechanism. The tax law stipulates that the procedures for tax dispute resolution are protest, arbitration, and judicial judgment.
● Protest
Taxpayers who are dissatisfied with the tax administration's reassessment or other decisions can lodge a protest with the head of the tax administration. The protest must be limited to facts or other information in the tax revaluation or other decision or tax revaluation process. Administrative protests must be filed in writing and must be submitted to the tax administration department within 30 days after the taxpayer receives the tax administration notification letter from the tax administration department. Only when the protest letter has the following contents can the administrative protest be accepted:
(1) The ID number of the taxpayer who wrote the protest letter;
(2) Evaluation, determination or reference proof of the results of the object of the protest letter;
(3) The fact or behavior of the object of the protest;
(4) Reasons for protest;
(5) Date and signature of the taxpayer and the signature of the taxpayer’s authorized agent, if necessary.
Administrative protest cannot relieve taxpayers of any obligation to pay various taxes, surcharges, and interest as stipulated in the tax collection and administration notice letter. After receiving a protest letter used to determine the tax valuation or other all or part of the taxpayer’s protest, regardless of whether the protest letter is correct or not, the tax administration must make a new decision within 60 days after receiving the protest letter.
● Arbitration
If the taxpayer does not accept the new decision of the tax administration, it can submit a letter of protest to the Tax Arbitration Commission within a 30-day period.
● Judicial judgment
After receiving the decision of the Tax Arbitration Commission, the taxpayer has the right to appeal to the competent court within 30 days of the decision. Taxpayers must deposit security deposits in the country before applying to the courts. The amount is equivalent to the amount of taxes, surcharges and interest assessed by the tax administration in the dispute.
Violation of the tax law
● Illegal
If the taxpayer or withholding agent pays less than 10% of the tax stipulated in the tax clause, it will be considered an illegal act.
If the taxpayer or the withholding agent fails to report or pay taxes in a timely manner within the specified time, it will be considered an illegal act.
● Serious violation
If the taxpayer or withholding agent pays less than 10% of the tax stipulated in the tax provisions, it is considered a serious violation of the law.
● Tax evasion
Tax evasion refers to repeated and repeated violations of the law with the knowledge of the situation, and the purpose is to deliberately reduce and eliminate the tax payable required by the tax clause. The serious violations referred to in Section 7.2 are also considered tax evasion under the following circumstances.
① It happened twice in the three months of the actual calendar year.
②In any period of time, there are three or more occurrences accumulatively.
● Acts that deliberately hinder the implementation of the tax law
Deliberately obstructing the implementation of the tax law as follows:
1. In terms of natural persons:
①Failed to keep normal accounting books and other related documents or did not issue invoices during the transaction.
②Do not allow tax authorities personnel to have access to accounting books and other related documents.
③Not registered with the tax authority.
④ Failure to promptly notify the tax authorities of changes to the registration materials in accordance with the law.
⑤ Manufacturing and reporting forged records, document reports or other information materials.
⑥ Concealing or deliberately destroying the accounts, records, documents, reports and other related materials in the accounting books.
⑦ Attempt to prevent tax assessment or tax collection.
⑧Cannot submit a complete tax report within 30 days required by law.
⑨ Deliberately support the above-mentioned obstructive behaviors.
2. As a government official:
① Leak confidential information without authorization.
② Attempts to hinder the assessment of tax authorities and the collection of taxes.
③ Deliberately support the above behavior.
● Criminal offenses that violate the tax law
Regardless of the penalties of other administrative provisions, anyone who engages in tax evasion activities according to Clause 7.3, or anyone obstructs the operation of the tax system according to Clause 7.4, is a criminal act that has violated the tax law.
additional tax
If the taxpayer pays insufficient taxes or delays the payment of taxes or obstructs the implementation of the tax provisions, additional taxes will be imposed.
● Additional tax added due to insufficient tax payment
For those who violate the law, a 10% tax will be added as an additional tax for the insufficient payment. If the part less than one month is counted as one month, 2% interest will be paid every month. For serious violations of the law, 25% of the tax will be added to the insufficient payment as an additional tax. If the part less than one month is counted as one month, 2% interest will be paid every month. During the tax revaluation period or within 30 days after the issuance of the tax collection notice, no interest will be added.
● Additional tax added due to late payment of tax
Taxpayers who have not paid taxes due, will be subject to an additional 10% late fee as an additional tax, and an additional 2% monthly interest on the unpaid tax will be levied. If the part is less than one month, it will be counted as one month. If the taxpayer has not paid the tax within 15 days after receiving the dunning notice, 25% of the late payment fee will be added as a surcharge, and the amount of less than one month will be calculated as one month, and an additional 2% interest will be paid. If the taxpayer does not declare the tax, the tax authority can directly assess the tax payable. In this case, the taxpayer will be subject to an additional 40% of the assessed tax. The amount of less than one month will be calculated as one month, and another 2% will be paid for one month. interest.
The interest of late payment of tax shall be calculated from the first day of the next month when the tax should be paid, and the interest of the late payment of profit tax shall be calculated from the first day of the month following the end of the tax annual report. The additional tax arising from the payment is 100% of the tax payable.
● Additional taxes levied for obstructing the implementation of tax clauses
The additional tax fines imposed for obstructing tax enforcement are as follows:
(1) Taxpayers or withholding agents will be fined 2 million Khmer for obstructing government officials from performing tax assessments.
(2) Taxpayers or withholding agents will be fined 500,000 KRW for hindering government officials from performing simple or estimated tax assessments.











