This service account insists on originality. The author is Zhang Xiaoming, partner of Zhuozhi (Cambodia) Accounting Firm, three years of multinational enterprise management experience, six years of listing audit experience, five years of entrepreneurial experience, Chinese certified public accountant (CPA), international certified public accountant (ACCA) ). WeChat: 13928404895, 085502018
Cambodia's main taxes
Profit tax
● Overview
| Taxpayer
Profit tax applies to all tax residents in Cambodia. The definition of "tax resident" is:
(1) Anyone who has lived in Cambodia for a long time or has lived in Cambodia for more than 182 days in the tax year (12 months). (2) Any legal person that organizes and operates various commercial activities and cooperative operations in Cambodia or the main business activities in Cambodia.
| Taxation object
The income of Cambodian tax residents derived from domestic and foreign income is the subject of profit tax. Including: profits earned by individuals or companies operating any trading activities and interest, rent or other legally obtained income from investment activities.
| Taxation mechanism
The taxation mechanism is as follows:
(1) For the assessment of profit taxation, the tax administration agency will review the actual taxation mechanism (verified collection procedure), or simplified mechanism (simple collection), or estimation mechanism (approved collection).
(2) The taxpayer adopts one of the three assessment mechanisms mentioned above, and the government implements the amendment and supplementary bill. The government will consider the taxpayer’s business model, industry, business activities and business when implementing the tax collection method. The amount of scale.
● The rate of tax payable on profit
| Tax Year
Decision of tax year:
(1) If the actual actual taxation mechanism is adopted, the profit tax payable this year will be included in the calculation of the undeclared part of the asset balance final statement declared in the previous year.
(2) If any year's final balance sheet of assets is not calculated as the tax payable in the coming year, the accumulated profits should be calculated from the last tax payment to the last day of the taxable period. For newly established enterprises, it is calculated based on the cumulative profits generated from the start of business to December 31 of the year.
(3) If there are multiple asset balance final accounts in the same year, the total of these final accounts shall be used as the tax calculation base.
(4) The calculation method of profit tax under the simplified and estimated mechanism is calculated based on the accounting statement data of the previous year.
(5) The detailed information and procedures for filing and filing required for the termination of activities, reorganization, sale and transfer of relevant enterprises within the tax year shall be announced by an administrative order issued by the Ministry of Finance and Economics.
| Taxable Profit
The profit subject to profit tax refers to the net profit generated by the enterprise as a result of various business activities, including asset appreciation, corporate activities, business closure or sales of some assets, as well as the income generated by the enterprise when it makes financial investments. Such as interest, rent and royalties.
| Income exempt from taxation
Except for specially stated terms and profits derived from indirectly related businesses, the following organizations are exempt from profit tax:
(1) The income of the Royal Government and the agencies under its jurisdiction.
(2) The income of the following organizations.
①The income of religious organizations, charities, scientific undertakings and educational undertakings.
②The income of the organization does not include the personal income of the personnel of the beneficiary organization, or any cash income and asset income for personal use.
3) The income of labor organizations, business associations, industrial associations, and agricultural associations, which are not used as the private income of members of these organizations or the income of organizations for personal use.
(4) Taxpayers who do not adopt the actual actual tax payment mechanism, the income derived from the sale of their own agricultural products or extension products of traditional agricultural products (agricultural products whose nature is changed through industrial processing methods). The packaging of agricultural products to extend the shelf life cannot be regarded as an extension of traditional agricultural products.
(5) Dividends derived from domestic enterprises refer to the income provided in Article 20, Article 23 and Article 26 of the Tax Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia (after all taxes payable have been paid).
● Pre-tax deduction
| Allowable deductions
The allowable deductions are as follows:
(1) Except for items 1.3.2 to 1.3.8, the items allowed for pre-tax deduction include the expenses or costs paid by the taxpayer for the sustainable development of business activities during the tax year.
(2) The rent, interest, compensation, payment or other expenses paid to directors or managers of any enterprise, distributors, taxpayers' family members or other related persons, as long as they are true and reasonable in price, can be paid in tax Deduction before tax during the year.
(3) The funds used to purchase new real estate and other tangible assets, and to update durable equipment, including loan interest and taxes arising from the purchase of real estate, can be recorded as special items during the tax year and accrued in accordance with 1.3.3 Depreciation, depreciation expenses can be deducted before tax in the tax year.
| Interest Expenses
The loan interest paid for normal production and operation can be deducted before tax in the tax year. The interest expense cannot exceed the sum of the taxpayer's net profit or 50% of the taxpayer's non-interest net income during the tax year. The non-interest net income referred to here refers to the total operating income after net profit is deducted, minus allowable expenses and costs (excluding interest paid). The balance of interest expenses mentioned above that cannot be deducted can be included in the next tax year and continue to be deducted before tax. Its principles and methods must still be carried out in accordance with the provisions of this clause.
| Tangible Assets
The tangible assets are as follows:
The first category: the building and its structure and its components, the depreciation rate is 5%, and the straight-line depreciation method is used.
The second category: computers, electronic information systems, software and data exchange equipment, the depreciation rate is 50%, and the balance declining depreciation calculation method is adopted.
Three categories: cars, trucks, office furniture and equipment, the depreciation rate is 25%, using the method of balanced declining depreciation.
Type 4: Other types of tangible assets adopt a depreciation rate of 20% to balance the declining depreciation calculation method.
| Depreciation of intangible assets
Intangible assets include copyrights, blueprints, models, and the right to use chain stores. If the above-mentioned intangible assets have a certain useful life, the depreciation calculation method can be based on the characteristics of the respective intangible assets and the use life of the intangible assets, using the straight-line depreciation method to calculate the depreciation amount. If the time limit for use of intangible assets cannot be estimated, depreciation can be made at 10% of the value of intangible assets.
| Depletion of natural resources
The depletion of natural resources shall be handled in accordance with the following regulations: The depletion of reserves of natural resources (including oil and natural gas) shall be regulated as follows:
① All exploration and investment, including the interest arising from investment, are classified as natural resource asset projects.
②In the tax year, the amount of depletion of natural resources can be deducted before tax; the calculation method of the amount of depletion: the value of natural resource assets is multiplied by the ratio of the actual production quantity and the estimated total production of natural resources in that year.
③The procedures and methods for calculating and estimating the total amount of natural resources that can be produced shall be implemented by bills passed by Congress.
| Charitable Donations
The charitable donations applicable to the groups mentioned in 1.2.3 above can be deducted from the taxable income, and cannot exceed 5% of the total taxable income before the donation is counted. The government will pass legislation to implement bills on charitable donations.
| Recoverable loss
The loss in any tax year can be deducted from the taxable income in the next tax year; if the taxable income in the next tax year cannot offset this loss, the part of the loss that has not been offset can continue to be transferred to the next tax year It will be offset again until the fifth tax year. In the event of continuous losses for many years, the previous years' losses will be deducted in order according to the content of this clause.
| Sharing of income and expenses among affiliated companies
If there are multiple companies with co-owners, regardless of whether these companies are within or outside the Kingdom of Cambodia, the tax authorities under their jurisdiction shall allocate the owners’ gross income or deductions or other benefits among the respective companies to clearly reflect them. The income of these enterprises or business owners prevents tax evasion and tax avoidance. Among them: having a common owner means that the same taxpayer owns two or more enterprises and holds more than 20% of the equity value of the enterprise at the same time, and the taxpayer is the joint owner of these two or more enterprises.
| Deductions not allowed
The items that are not allowed to be deducted from taxable income are as follows:
(1) Any expenses considered to be related to entertainment and entertainment activities, entertainment activities or any expenses related to the above activities.
(2) Personal and family expenses, but excluding cash income from various additional incomes that have been fulfilled as required by the payroll tax clauses.
(3) Any tax levied in compliance with the provisions of the profit tax clause, or any tax withheld and paid in compliance with the provisions of the wage tax clause.
(4) Any loss incurred from property sales or mutual exchanges between related persons.
(5) The law clearly stipulates any other expenditures that actually occur in business activities and allow pre-tax deductions.
● Tax rates and taxes
| Annual profit tax rate
(1) 20% of the profits generated by any legal person.
(2) Oil and natural gas cooperative production, natural resource exploration, etc., including 30% of the profit generated from the mining and production of timber, mineral deposits, gold and gems.
(3) Qualified investment projects approved by the National Development Council of Cambodia will enjoy a 9% profit tax during the five-year transition period. It started in the tax year after the implementation of the Investment Amendment Act of the Kingdom of Cambodia.
(4) Enterprises with qualified investment projects approved by the National Development Council of Cambodia can receive a preferential tax holiday and a profit tax rate of 0%.
(5) Natural persons who are not "legal persons" and members of "loose cooperative management" will pay profit tax based on the following gradually increasing annual income based on the income reflected by their participation in the proportion of shares.
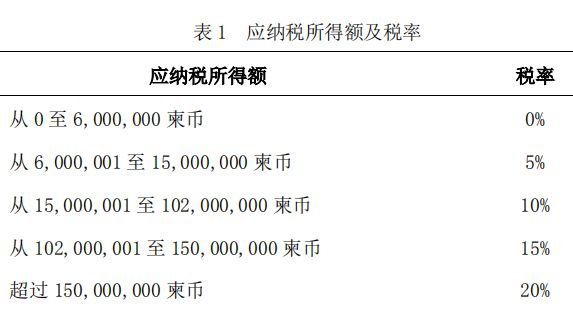
6) The Investment Amendment Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia stipulates that, except for business mergers and acquisitions, the powers and preferential policies granted by the government to taxpayers cannot be transferred or designated to a third party.
| Insurance Company Profit Tax
Insurance companies shall pay profit tax in accordance with the following provisions:
(1) Taxpayers engaged in insurance business activities, such as life insurance, reinsurance, property insurance or other risk insurance businesses, shall calculate and pay profit tax in accordance with the following clauses:
① 5% of the total value of insurance policies and reinsurances received within one year of the tax year in Cambodia.
② Other non-insurance business or reinsurance business activities shall be taxed in accordance with the requirements of 1.4.1.
(2) The procedures and methods of profit tax levied on insurance companies will be announced and implemented through government orders issued by the Ministry of Finance and Economics.
| Profit tax on non-main business income
Non-business income is subject to the following taxes: The non-business income of the organization specified in Article 9 of the Kingdom of Cambodia Tax Law is taxed at a rate of 20%.
(1) Non-operating income tax refers to the total income of an enterprise or organization from operating activities that have nothing to do with its main business, after deducting the expenses permitted in its profit tax clause.
(2) "Irrelevant business (non-business business)" refers to commercial or industrial manufacturing, or other business carried out by enterprises and organizations for the purpose of obtaining profits or funds, but the business is related to The main business purpose or business function of the tax exemption provided in Article 9 is not significantly related.
● Additional surcharges
During the tax year, the enterprise will donate to domestic or foreign shareholders, and may incur additional tax. The tax calculation basis is based on the possible tax law multiplied by the product specified in Article 20 of the "If Foreign Tax Law".
Note: Article 20 of the Tax Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia: The annual profit tax rate is as follows:
The income realized by the legal person is 20%.
The income realized by the distribution of petroleum products and natural gas according to the contract or the operation of natural resources including wood, minerals, gold or various precious gems is 30%.
The income realized by the investment company beyond the tax exemption period is 9%.
The income realized by the investment company within the tax-free period is 0%.
According to the following tiered tax rate table, it is for the income realized by natural persons and the income part of the business group that is not considered as a legal person to distribute to each member.
Annual taxable income tax rate%
From 0 to 6000000 (Khmer currency ) 0%
From 6000001 to 15000000 (Khmer currency) 5%
From 15000001 to 102000000 (Khmer currency) 10%
From 102000001 to 150000000 (Khmer currency) 15%
More than 150,000,000 (Khmer currency) 20%
● Tax liability
| Taxpayers’ obligations assessed on a real basis and simplified basis
1) All taxpayers subject to profit tax must carry out tax assessment on a real basis or on a simplified basis to carry out tax assessment requirements to calculate and pay their profit tax. The profits obtained must be declared to the tax authorities within three months after the end of the tax year.
(2) The tax assessment report submitted to the tax authority on a true basis must include:
①Financial balance sheet
②Project settlement report
③Auxiliary voucher data report
(3) The tax assessment report submitted to the tax authority on a simplified basis must be completed in accordance with the tax form provided by the tax authority and the required attachments.
(4) A loss-making enterprise must also submit relevant information to the tax authority in the same reporting method and time limit requirements.
| Taxpayers’ obligations assessed on an estimated basis
(1) Taxpayers assessed on the basis of estimates must submit their tax statements to the tax authorities before December 31 each year in accordance with the format required by the tax administration agency.
(2) After the tax authority has reviewed, confirmed and negotiated the information submitted by the taxpayer or its agent, the tax authority will determine the taxpayer’s income. The calculation method of the amount of income is calculated based on the taxpayer's business category and the approved profit rate. The detailed rules shall be implemented by the administrative order issued by the Ministry of Finance and Economics.
(3) The applicable profit tax rate will remain unchanged for a certain period of time, three months, six months or one year.
(4) Taxpayers who adopt the estimated taxation mechanism must pay profit tax on a fixed monthly date set by the tax authority.
| Obligations of natural persons to withhold profit tax
If a natural person is required to withhold the profit tax, in accordance with the instructions of the tax authority, within the fifteenth day of the month following the occurrence of the profit tax obligation, the tax authority shall pay the withheld profit tax to the tax authority. Citizens’ taxable income items:
(1) All kinds of income paid by domestic enterprises or domestic "subcontracting" or government agencies.
(2) Dividends distributed by domestic enterprises.
(3) Income from the provision of services (labor services) in Cambodia.
(4) Remuneration for management services and technical services paid by residents.
(5) Income from fixed and non-fixed industries in Cambodia.
(6) Royalties of patent rights and intangible assets paid by Cambodian enterprises controlled by residents or non-residents.
(7) Income from the sale of Cambodian industries or the transfer of fixed industries in Cambodia.
(8) Insurance policy fees paid for risks or reinsurance in the Kingdom of Cambodia.
(9) Income received by non-resident taxpayers in Cambodia from the sale of their fixed or mobile assets in the Kingdom of Cambodia.
(10) Income from non-residents who conduct business through fixed corporate institutions in the Kingdom of Cambodia.
● Calculation method of annual tax payable
| Deduction of foreign taxes paid
(1) Resident taxpayers whose income comes from abroad and have paid foreign taxes according to the requirements of foreign tax authorities may deduct the taxes paid abroad from the profit tax calculated in Cambodia; the taxpayer must issue a certificate Relevant documents and materials of tax paid abroad.
(2) In Cambodia, when calculating the tax payable, taxpayers must first calculate the total amount of income derived from Cambodia’s domestic income and income derived from abroad, including excluding taxes paid abroad.
(3) Tax deductibles paid by Cambodian tax residents from foreign income from different countries will be treated individually; the tax deductibles used for deduction in the tax year must meet the following condition:
① The amount of taxes actually paid abroad.
②The amount of tax deductible is based on the sum of all profit taxes paid during the same period as mentioned in 1.4.1, multiplied by the ratio of income from abroad and the sum of all income. The procedure for confirming the amount of tax deductible requires the provision of relevant documents, including tax payment certificates or payment vouchers issued by foreign tax authorities.
When the amount of tax deductible is greater than the tax payable on profit, the remaining amount of tax deductible that cannot be offset will be set aside for the next tax year for offsetting, and the cycle will continue to offset until the fifth year. Starting from the year in which the tax deductible is incurred, the tax deductible is more than the tax payable for profit in the year in which the tax deductible is processed gradually according to the principle of first occurrence, first offset.
| Steps to calculate profit tax
The following are the steps to calculate the profit tax payable:
(1) Calculate the total amount of all taxes payable in accordance with 1.4.1 and 1.5.
(2) In accordance with the content of 1.7.1, subtract the tax credit of foreign taxes, but not exceed the total amount of foreign taxes paid.
● Minimum tax
The minimum tax is levied on taxpayers who conduct tax assessments on a real basis. The minimum tax is different from the profit tax. Taxpayers who conduct tax assessments on a real basis must pay the minimum tax even if they are granted the legal status of an investment enterprise. The minimum tax is levied at 1% of the annual turnover excluding all taxes and is paid when the profit tax year is settled.

Payroll tax
● Overview
| Taxpayer
Any natural resident of the Kingdom of Cambodia is obliged to pay wage tax regardless of whether the salary is from domestic or foreign sources.
Any natural resident who is not a natural resident of the Kingdom of Cambodia shall pay payroll tax on salary originating in Cambodia.
| Taxation object
Payroll tax is a monthly tax levied on salaries received from employment activities. "Salary" refers to the salary, remuneration, wages, bonus and compensation for overtime work and other various additional benefits directly paid by the employer to the employee due to the employee's obligation to complete the employment activities.
● Exemption from payroll tax
| Salaries of diplomats and other foreign officials
The conditions for exemption of payroll tax for diplomats and foreign officials are as follows:
(1) Officials who are exempt from salary tax are as follows:
①Foreign government officials or diplomatic personnel or consulates who are holding diplomatic passports or government officials' passports issued by the foreign government while in the Kingdom of Cambodia complete their official assignments and receive remuneration.
②Salaries and remunerations received by foreign representatives in Cambodia, personnel employed by international agencies or agencies of other countries to complete their official tasks within Cambodia.
(2) Any payroll tax exemption measures permitted in this item must be implemented under the premise that the country of the beneficiary has the same arrangement for Cambodian nationals.
| Employees' income exempt from payroll tax
The matters that can be exempt from payroll tax are as follows:
(1) For the benefit and arrangement of the employer, the actual salary paid to the employee under the conditions of the following three clauses:
① Directly and fully represent the interests of the employer's enterprise;
②There is no increase or decrease in false reports;
③Issuing the paid settlement invoice, the name must be the name of the person who actually accepts the claim;
(2) Compensation for dismissed persons within the limits set by the "Labor Law";
(3) Under the terms of the labor law, the additional remuneration generated by social service activities.
(4) Provide free or purchase uniforms or professional equipment that are lower than the actual selling price.
(5) A fixed allowance for tasks or travel expenses. The fixed allowance does not overlap with the actual reimbursement amount in this clause.
● The tax base and conditions of payroll tax
| Taxation basis of payroll tax
In addition to the welfare income stipulated in Article 48 of the Tax Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia, the taxation basis for the salary tax paid by residents is the taxable salary income deducting the following items:
(1) In order to comply with the relevant provisions of the Labor Law, part of the salary, pension and social welfare funds are withdrawn in advance.
(2) The following items are allowed for exemption from taxation.
| Taxable Salary Income
The monthly taxable salary is determined by the following conditions:
(1) The monthly taxable salary income of resident employees includes:
①Income from Cambodia.
②Income from abroad.
③The advance payment provided by the employer to the employee, such as a loan or instalment payment, is on receipt
The month of the said payment shall be included in the taxable salary income; the employee shall deduct this repayment from the taxable salary income in the month in which the above payment is returned.
(2) Any resident employee can enjoy the following salary deductions according to his actual family status:
① For children who have minors and still need to be supported by taxpayers, 75,000 riel/person can be deducted from the salary tax base.
②The spouse of an employee who only engages in housework can deduct 75,000 riel from the taxable salary income base per month, and only one spouse is allowed.
(3) For non-resident taxpayers, taxable salary income from Cambodia is handled in accordance with the provisions of this chapter.
| Tax Rate
For employees who are residents, the applicable tax rate of their taxable salary income depends on the amount of taxable salary income; employers must withhold taxes for employees, withholding and paying the amounts and tax rates listed in the following table.
| Tax rates applicable to dividends and bonuses
Employers are required to deduct all dividends and bonuses (extra income) due to the time based on the 20% tax rate; the value of the above-mentioned welfare income is the fair market value including all taxes.
| Deduction of foreign taxes paid
Resident taxpayers who accept foreign salaries and have paid foreign taxes in accordance with the requirements of foreign tax authorities can be deducted from Cambodia’s payroll tax. They must submit tax payment vouchers and receipts issued by foreign tax authorities.
● Responsibilities and obligations of employers and employees
| Responsibilities of withholding tax (withholding and paying) person
The responsibilities and obligations of payroll tax withholding and payment are as follows:
(1) Legal representatives, including foreign legal representatives, are obliged to withhold and pay the payroll tax; if the content of this clause is inconsistent with the content of the international contract, it will be dealt with separately.
(2) Employers should withhold and pay wage tax when paying salaries, and submit them to the national treasury uniformly.
(3) Employers living abroad can appoint an agent in Cambodia to act as the person in charge of withholding and paying wage tax when paying salaries, and be responsible for turning over the withholding tax collected to the national treasury.
(4) Regardless of whether the salary is paid in Cambodia or abroad, the employer or foreign employer’s agent in Cambodia and its employees are obligated to pay withholding wage tax; if the withholding tax is not paid in accordance with the regulations, this clause The prescribed employer shall be responsible for urging the employee to pay the payroll tax, but the employer still bears the legal responsibilities and obligations stipulated in this clause.
| Withholding tax payment
The deducted payroll tax shall be paid to the tax authority in the place where the employee's domicile is registered or to the tax collector designated by the government agency within 15 days of the month following the payment of the salary.
| Record keeping and reporting of withholding tax
All employers who pay salaries to employees have the following responsibilities:
(1) Calculate the taxes that should be withheld and paid before salaries are paid.
(2) Report the progress of the payment of withholding taxes to both the tax administration agency and the employees.
(3) The record vouchers and account books of withholding taxes are kept, and the specific content and method will be announced and implemented by the Ministry of Finance and Economics through an administrative order.

● Taxpayer
According to Article 60 of the Tax Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia, a taxpayer refers to a person who purchases goods and services that are subject to VAT when conducting tax assessments on a true basis. Anyone who adopts the estimated basis for tax assessment can apply to become a taxpayer. The required conditions and application procedures will be announced and implemented by the Ministry of Finance and Economics through an administrative order. Within this clause, employees who engage in activities that are purely personal are not taxpayers.
● Taxable goods and services
Except for special other notes, the "taxable goods and services" referred to in the clauses of this chapter are:
(1) Goods and services provided by taxpayers in Cambodia.
(2) Self-produced products or goods used by the taxpayer.
(3) Items given by the taxpayer as gifts, or goods or services provided below cost.
(4) The management procedures and laws applicable to imported goods under the jurisdiction of the Cambodian tax authorities shall be revised and passed by the National Assembly.
● Tax exemption
Tax exemptions include:
(1) Public postal services.
(2) Hospitals, clinics, dental medical services, and services that provide the above-mentioned multiple services and sell medical, dental and other medical supplies.
(3) The public transportation passenger service system operated by the state.
(4) Insurance services.
(5) The specific contents of basic financial service items shall be announced by the Ministry of Finance and Economics through administrative notices and orders.
(6) Imported goods that meet the requirements of the administrative order issued by the Ministry of Finance and Economics and are exempt from customs duties.
(7) Non-profit activities that are related to the public interest approved by the Ministry of Finance and Economics.
● Duty-free items for diplomats and international organizations
The regulations on duty-free items for diplomats and international organizations are as follows:
1) Foreign envoys, consular staff, international organizations, and technical cooperation agencies must import goods that must be imported as duty-free items for the performance of their official duties. For the duty-free items to be imported, the chief of the above-mentioned group of the imported items shall issue a certificate to the taxation department and indicate the name and purpose of the imported items, and the import can only be processed after approval. If you need to import duty-free items, the personal items used as members of the above-mentioned groups or organizations are limited to the types of items in the list of permitted imported goods announced by the administrative order of the Ministry of Finance and Economics. The implementation of the provisions on duty-free items in this clause must be carried out in the principle of reciprocal implementation of relevant countries.
● Tax rate and tax determination
| Value-added tax rate
The tax rates are as follows:
(1) Within the Kingdom of Cambodia, the VAT rate applicable to any taxable goods is 10%.
(2) According to Article 63 of the Tax Law of the Kingdom of Cambodia, all taxable goods exported from Cambodia or taxable services exported abroad are subject to a 0% value-added tax rate. The taxpayer shall provide the tax authorities with the export documents and certificates, including the export documents and certificates issued by the customs; the import documents issued by the country where the goods are imported; the executed remittance letter of credit and the evidence of payment received by the domestic bank.
| Credit for input tax on the purchase of imported goods or services
requirement is:
(1) The tax paid by taxpayers who purchase goods and services for the purchase of goods or services required for business operations can be deducted from the value-added tax payable when selling goods and services.
(2) If part of the purchased goods or services includes tax and the other part is exempt, only the tax-included part is regarded as the deductible tax part.
| Confirmation of VAT
Confirmation conditions of the value-added tax amount:
(1) The taxes levied under 3.5.1 are the national debts borne by taxpayers.
(2) The tax payable is the balance of the output tax calculated based on the tax rate in 3.5.1 minus all input tax deductions allowed in the current month.
| Documents required to declare the tax credit for imported goods
(1) Submit value-added tax invoices in accordance with the requirements of 1.3.8 above.
(2) All customs clearance documents for imported goods, including the import tax payment certificate issued by the customs containing the name of the consignee.
| Imported goods or services that are not tax-refundable (deductible)
Taxes included in imported goods or services that are not eligible for tax rebates (tax deductions) include taxes payable by taxpayers in social, recreational and entertainment activities.
● Tax declaration and payment
| VAT declaration
Taxpayers must fill in the previous month’s VAT report within the 20th day of the following month after the end of each month, and report to the tax authority.
| Treatment of input tax greater than output tax
According to the tax law of the Kingdom of Cambodia, the taxpayer pays input tax that is greater than the output tax received by the taxpayer in any month: part of the input tax greater than is used to offset the taxpayer's unpaid value-added tax in the previous month; The deducted input tax can be used as the input tax of the following month to continue to be deducted.
| Payment of Taxes
The relevant tax payment regulations are as follows:
(1) Any taxpayer or person who imports goods shall pay taxes and pay other taxes payable related to taxable goods or services in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 3.5.1 above.
(2) If the taxable goods supplier does not have any other business activities in the Kingdom of Cambodia, and the tax agency encounters obstacles in collecting taxes from the goods supplier, it will clearly stipulate this special situation through an amendment bill Processing procedures.
(3) Anyone who supplies goods on behalf of the employer as an employee and has the right to supply goods, and the goods supplied are taxable goods.
Other major taxes
● Specific goods and services tax
● Lease tax on land and house
Businesses engaged in land and building leasing are obliged to pay land and house leasing taxes. The lease tax on land and houses is calculated on the basis of the rental income obtained by those engaged in the leasing of land and houses, and the tax rate is 10%.
● Stamp Duty
Stamp duty is levied on specific official documents, specific advertisements, etc. The amount of tax depends on the place where the advertisement is set up, the lighting used, and the national language. In addition, when transferring specific assets such as free land, heavy and light trucks, cars, motorcycles, yachts, etc., stamp duty is paid at 4% of the transfer value.
● Unused land tax
Unused land tax refers to the taxation of unused land on the land in cities and designated areas that has not been constructed, or has buildings that are not used, and the unused land of specific development sites. The tax amount is changed from unused land on June 30 each year. The Evaluation Committee decided that, based on 2% of the market price per square meter of land, land within 1,200 square meters is exempt from tax. Owners of taxable land must pay the unused land tax before September 30 of each year.
● Transportation tax
The vehicle tax is a tax levied on specific vehicles such as trucks and ships at the time of registration.

Taxation Risks and Preventive Measures of Chinese Residents (Enterprises) Investing in Cambodia
Taxation Risks of Chinese Residents (Enterprises) When Investing in Cambodia
The Cambodian tax system has been formed in a relatively short period of time. Its characteristics are that there are more types of taxes and laws and regulations often change. These laws and regulations are usually unclear, contradictory and require interpretation. Usually, different branches of the tax department will give different explanations. Taxation is subject to review and investigation by different branches of multiple taxation departments. Tax officials lack experience in handling international tax affairs. Reassessment of taxes when dealing with matters outside the domestic business environment is usually arbitrary, and there are fewer written responses to questions raised by taxpayers.
The time for the formation of the income system is relatively short. Its characteristics are that there are more types of taxes and laws and regulations often change. These laws and regulations are usually unclear, contradictory and require interpretation. Usually, different branches of the tax department will give different explanations. Taxation is subject to review and investigation by different branches of multiple taxation departments. Tax officials lack experience in handling international tax affairs. Reassessment of taxes when dealing with matters outside the domestic business environment is usually arbitrary, and there are fewer written responses to questions raised by taxpayers.
How to prevent and avoid these risks
To prevent and avoid the tax risks of investing in Cambodia, Chinese residents (enterprises) must first fully understand Cambodia's tax laws and regulations, and keep abreast of the changed laws and regulations in a timely manner. Secondly, Chinese residents (enterprises) can seek help from local tax intermediaries with strong business capabilities. They have a better understanding of local tax laws and regulations and the duties of local tax authorities. Therefore, they are more capable of preventing and evading local taxes. risk.







