This service account insists on originality. The author is Zhang Xiaoming, partner of Zhuozhi (Vietnam) Accounting Firm, three years of multinational enterprise management experience, six years of listing audit experience, five years of entrepreneurial experience, Chinese certified public accountant (CPA), international certified public accountant (ACCA) ). WeChat: hy945568
Recently, customers often ask me: "What taxes should I pay in Vietnam", "how much", "can I refund the tax on imports" and so on. Many customers even ask: "If I pay in Vietnam If you register a company in the name of a person, will the tax be less?" Today, I will give you a complete answer to these questions.
What are the taxes generally paid in Vietnam?
Vietnam's tax laws must be approved by the National Assembly before they can take effect. The State Administration of Taxation and the Customs are the two directly affiliated agencies responsible for tax collection under the leadership of the Ministry of Finance. The customs is responsible for the collection of customs duties, and the State Administration of Taxation is responsible for the collection of domestic taxes. There is no distinction between central tax and local tax in Vietnam.
Both foreign-invested enterprises and domestic-funded enterprises in Vietnam adopt uniform tax standards, and implement different tax rates and tax deduction periods for projects in different fields.
Vietnam’s current tax laws and regulations have the following taxes and fees: value-added tax, special consumption tax, corporate income tax, personal income tax for high-income groups, non-agricultural land use tax, land use right transfer tax, agricultural land use tax, housing land tax, Resource tax, stamp duty, import and export tax, land use surcharges, etc., among which four types of taxes, corporate income tax, personal income tax, house tax, and value-added tax, apply to all enterprises. Below we will explain in detail these four types of taxes
corporate income tax
Starting from January 1, 2016, the basic corporate income tax (EIT) rate in Vietnam is 20%.
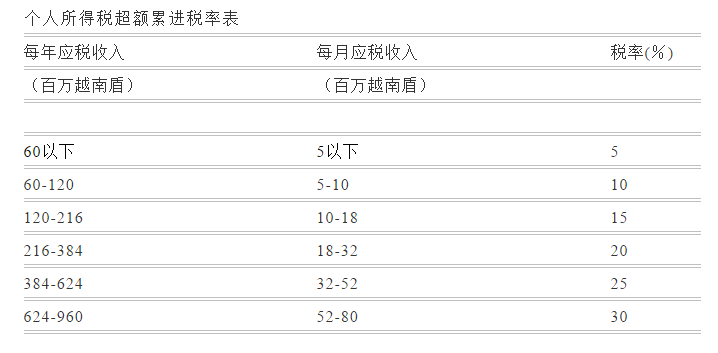
Personal Income Tax
House tax
House tax is a tax that must be levied every year for companies of various natures. House tax is based on the registered capital of the company. The tax for the year is paid at the beginning of each year according to a certain percentage of the company's registered amount. The maximum payment is 3 million VND. The registered capital is over 10 billion VND (approximately USD 500,000) and 3 million VND (approximately USD 150) is collected, and the registered capital is between 2 billion and 5 billion VND (approximately USD 100,000 to 250,000), and 1.5 million VND is collected Vietnamese dong (approximately 75 U.S. dollars); under 2 billion VND (approximately 100,000 U.S. dollars), 1 million VND (approximately 50 U.S. dollars) will be collected. Newly established companies that complete tax registration in the first half of the year and obtain a tax identification number will be levied stamp duty for the entire year, and will be paid at 50% in the second half of the year. For individuals, a tax rate of 0.5% to 2% applies when assets are transferred. Generally, the house number tax must be paid within 15-30 working days after the business license is issued after the company is registered, otherwise there will be a fine, which will be paid by the end of January the following year.
VAT
The value-added tax rate is divided into zero tax rate, 5%, 10% (basic tax rate) and 20%. The zero tax rate applies to export goods, the 5% tax rate applies to agriculture, medicine, health education, science and technology reporting, etc., and the 10% tax rate applies For petrochemical, electronics, chemical machinery manufacturing, construction, transportation, etc., the 20% tax rate applies to jewelry, hotels, restaurants, tourism, lottery, intermediary services, etc.
Tax refund
Since July 1, 2016, VAT refunds are only allowed under the following circumstances:
The exporter's excess input VAT to be deducted exceeds 300 million VND. According to the company's VAT declaration period, tax refunds are given on a monthly or quarterly basis. For the input VAT corresponding to the export sales (in accordance with the VAT tax rebate conditions), the amount of tax refundable to the enterprise cannot exceed 10% of the export income. VAT refunds are not applicable to companies that import goods and export them without processing.
In the pre-operational stage, the new investment plan companies that adopted the deduction method and their accumulated VAT to be deducted exceeded 300 million VND. However, it does not include investment plans that do not meet the prescribed conditions, or the capital of the investment plan is not allocated in accordance with the regulations. Liquidation, bankruptcy, changes in corporate equity, changes in corporate form, mergers and acquisitions, mergers, spin-offs, and divisions. Certain ODA schemes have diplomatic exemptions, and foreigners purchase goods in Vietnam for consumption abroad. In other cases, when the company's input VAT exceeds the output VAT during the period, the excess part will be delayed to offset the future output VAT.
Entities in Vietnam can use pre-printed invoices, self-printed invoices or electronic invoices. The tax invoice template must contain the required items and need to be notified or registered with the local tax authority. For export goods, commercial invoices can be used instead of domestic tax invoices.




