This service account insists on originality. The author is Zhang Xiaoming, partner of Zhuozhi (Vietnam) Accounting Firm, three years of multinational enterprise management experience, six years of listing audit experience, five years of entrepreneurial experience, Chinese certified public accountant (CPA), international certified public accountant (ACCA) ). Customer Service WeChat: hy945568
This article briefly introduces Vietnam’s business environment and tax system, focusing on corporate income tax, capital gains tax, value-added tax, foreign contractor tax, as well as transfer pricing, tax supervision, and administrative penalties that are closely related to "going global" companies. Provisions, and on this basis, for Chinese companies preparing to invest in Vietnam, it reminds the risks and problems of tax payment, administrative procedures, labor quality, local infrastructure, cultural differences and other aspects that need to be paid attention to, so as to help companies reduce risks .
Vietnam investment environment
After more than 30 years of reform and opening up, Vietnam has turned from one of the poorest countries in the world to enter the ranks of middle-income countries. Vietnam joined the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (hereinafter referred to as "ASEAN") in 1995, joined the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) in 1998, and joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2007, plus gross domestic product (GDP) With key factors such as the substantial increase in the number of foreign investors, the effective improvement of infrastructure conditions, and the steady growth of foreign direct investment, Vietnam has become quite popular among foreign investors.
According to statistics, Vietnam’s economic development continues to show strong growth. Since 1990, Vietnam has been one of the fastest-growing economies in the world with per capita GDP growth, with an average growth rate of 6.4% since 2000. Despite the global economic downturn in recent years, Vietnam’s economy is still steadily improving. In 2018, its GDP growth rate reached 7.08%, and it maintained a steady development trend.
1. Vietnam has shifted from a centralized economic system to a market economic system, and coupled with a demographic dividend of approximately 97 million people, it has the advantages of a young labor force and an increasing disposable income in recent years. In addition, the Vietnamese government has been working hard to maintain a stable inflation rate. The inflation rate in 2018 was 3.5%.
2. The main engines driving investment in Vietnam include:
(1) Located in the center of Southeast Asia, the superior geographical location facilitates the development of commodity circulation and cultural exchange activities;
(2) Young and energetic, with a large number of well-educated and digitally proficient labor force, develop entrepreneurial culture, and open-minded;
(3) Competitive production costs compared with neighboring countries;
(4) Free trade agreements with major developed markets in North America, Europe and Asia;
(5) The government is committed to creating a stable social and political environment to create an attractive business environment for foreign investors;
(6) The economy is growing rapidly, and the nominal GDP growth rate from 2016 to 2018 remains between 6% and 7%. With the continuous and rapid development of Vietnam’s economy, Vietnam’s business environment has also been continuously improved, which is mainly reflected in the continuous improvement of the legal and regulatory system, speeding up the restructuring and reform of state-owned enterprises, actively signing free trade agreements, continuously attracting foreign direct investment, and giving play to labor and living costs. Advantages and other aspects.
The status quo of Vietnam's business environment
(一) Complete legal system
The Vietnamese government has been committed to improving laws and regulations to promote the internationalization, rule of law, and facilitation of the investment and business environment in Vietnam. Since the introduction of the new law on investment and enterprises in 2014, the Vietnamese government has issued many decrees and notices to provide more favorable market entry conditions.
(二) The reorganization and shareholding of state-owned enterprises
The Vietnamese government has been committed to promoting economic reforms. In recent years, the reform of state-owned enterprises has become an example of how the government can improve the performance of state-owned enterprises and promote economic development. The process of state-owned enterprise demutualization from 2016 to 2020 has been listed in Resolution 58/2016/QD-TTg
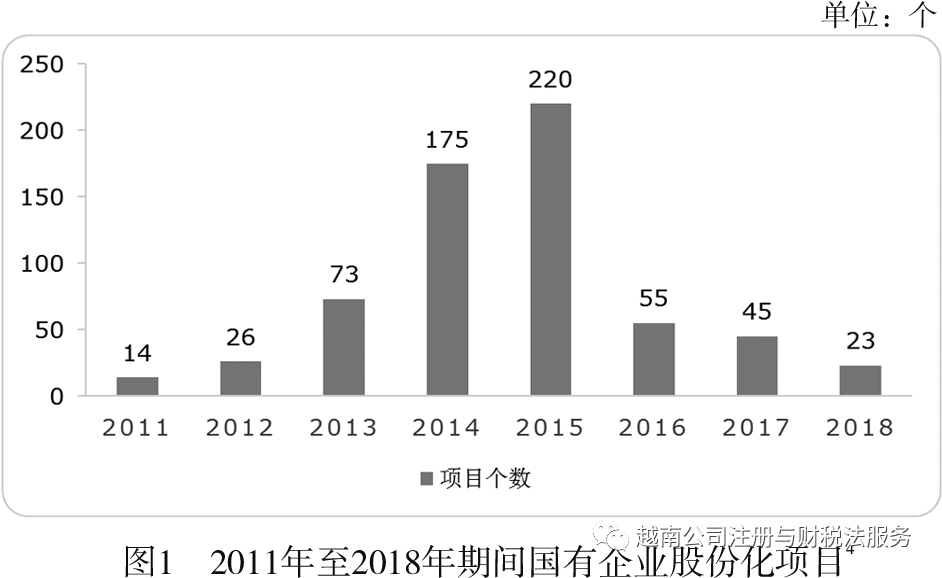
(三) The signing of a free trade agreement
In recent years, in order to accelerate the integration of the national economy with the global economy, the Vietnamese government has actively signed many free trade agreements, mainly including the following agreements:
1. The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), which was officially launched in December 2015;
2. The Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (CPTPP), signed on March 8, 2018;
3. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RECP), in coordination and communication;
4. In the name of ASEAN, sign free trade agreements with Japan, South Korea, India, Mainland China, Hong Kong, Australia and New Zealand;
5. With Chile, South Korea, Japan, Israel, and the European Union (approved in 2018 to negotiate and sign bilateral free trade agreements, the negotiation process for bilateral free trade agreements with the Eurasian Economic Union has ended, and coordination and communication with the European Free Trade Association are in progress. Currently, Vietnam has established diplomatic relations with more than 180 countries, established trade and investment relations with more than 220 economies, and signed more than 80 double taxation agreements.
(四)Foreign direct investment
Vietnam's total foreign direct investment in 2018 was 35.46 billion U.S. dollars. This is the sixth year that Vietnam's foreign direct investment projects have increased year-on-year, with 277 projects increasing by 26.5% 5. The continuous growth of foreign direct investment over the years means that investors’ confidence in the economic prospects has continued to increase. Vietnam is one of the few countries in Southeast Asia that is fully open to foreign investment. In addition, the Vietnamese government announced that between 2017 and 2020, 375 state-owned enterprises will be partially or fully divested.
(五) Labor and living costs
Vietnam has a population of over 97 million and is the 14th most populous country in the world. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of Vietnam, as of the end of 2017, the total working-age population in Vietnam was 48.2 million (50.7% of the total population), and the unemployment rate was 2.24%. There are huge differences in wages and salaries in various industries in Vietnam, as are the differences between urban and rural areas. The average monthly salary per capita in Vietnam is about 3.2 million VND (approximately US$150) 6. Compared with other Asian countries, the cost of living in Vietnam is still relatively low.




